Alona affinis
Alona affinis is the largest species in the genus Alona. It is a very common littoral species which is distributed in all parts of the country and found in all types and sizes of water bodies from sea level and up to alpine areas.
Key characteristics
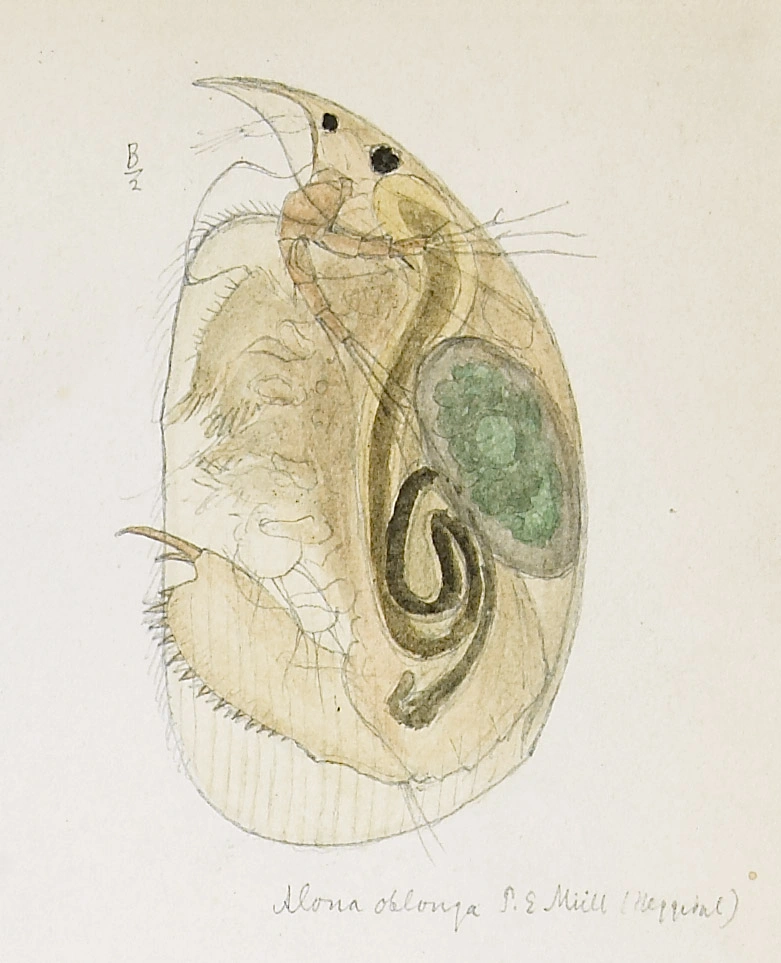
Alona affinis (female)
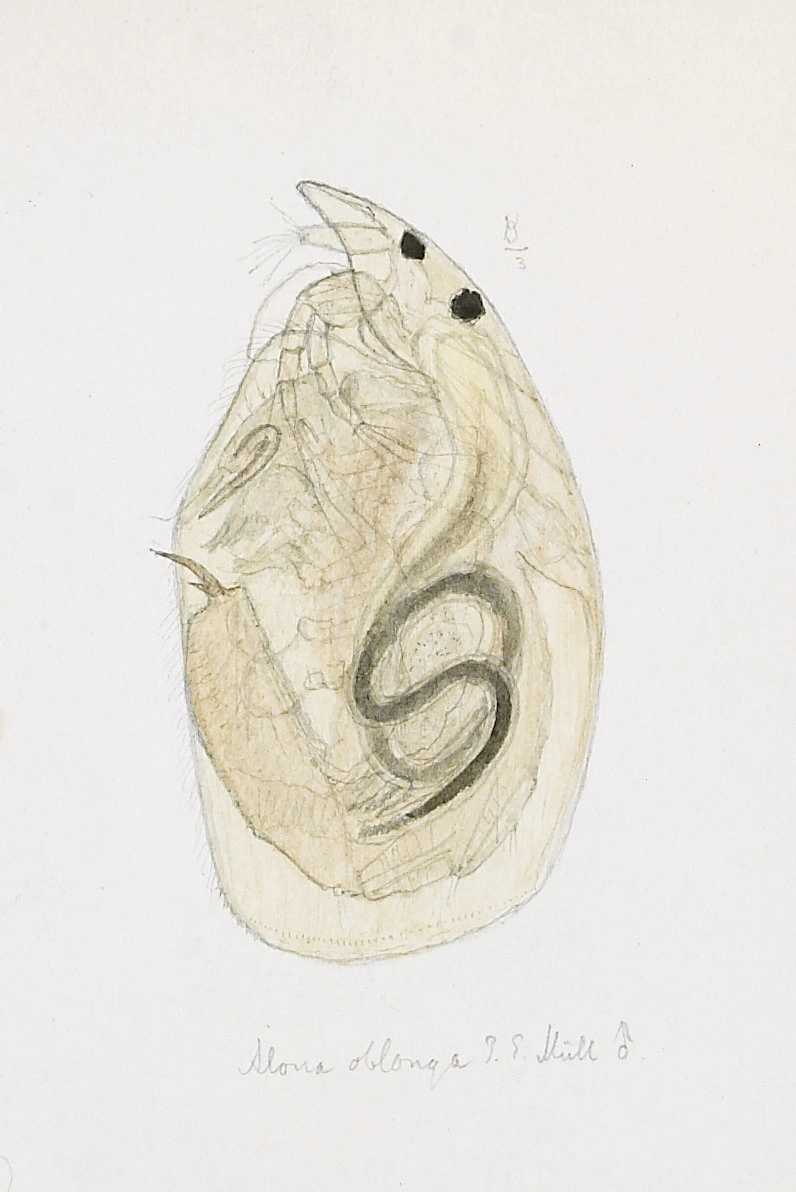
Alona affinis (male)
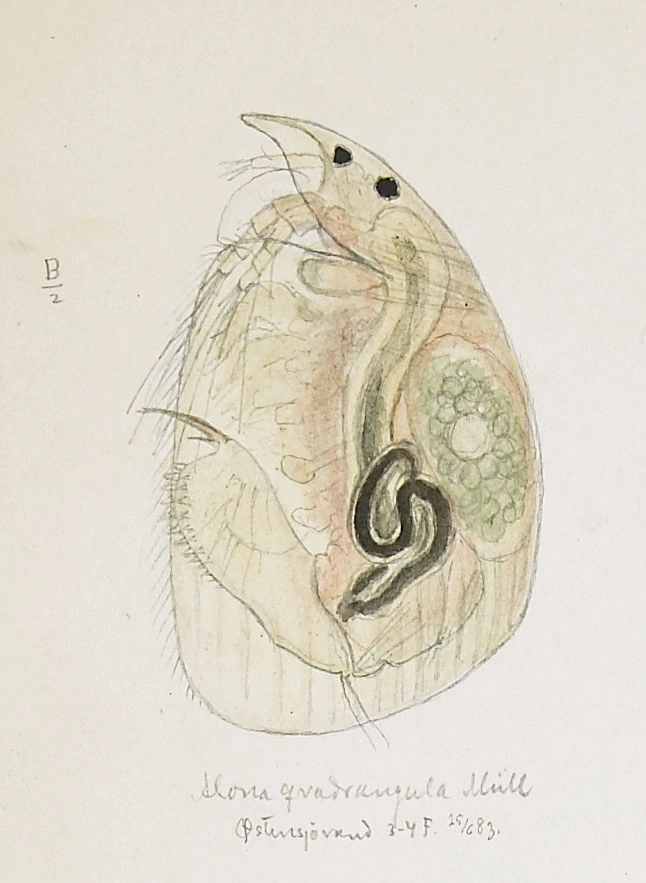
Alona affinis is the largest species in the genus Alona. Its postabdomen is vigorous, has an oval form and is similar to the postabdomen of A. quadrangularis with altogether 10–15 denticles. It differs from the latter species having 4–6 fine spinules on the basal spine close to the base in the abdominal claw. In contrast to A. quadrangularis, A. affinis has two instead of three head pores. Its colour varies, with brown and red as the dominating colours.
Female: Length 0.6–1.3 mm
Male: Length 0.7–0.9 mm
Ecology and distribution
A. affinis is a littoral scraper, which occurs in 43 % of the localities and is the most common of the Alona-species. It is distributed in all parts of the country from sea level and to 1396 m a.s.l., with the highest frequency at low altitudes. It’s common in all types and sizes of water bodies, and lives both in vegetation and on stony/sandy bottom. The species have a wide tolerance towards pH (pH 3.9–pH 9.1). A. affinis has been found in brackish water (957.0 mS/m) and occurs also in very dilute mountain waters (0.4 mS/m).
Conductivity (m S/m)
Surface area (da)
Elevation (m a.s.l.)
Look-alikes
Alona quadrangularis