Acanthocyclops robustus
Acanthocyclops robustus has a scattered distribution and is found in all parts of the country. It occurs in waters of varying sizes, being most common in small ponds. It is known as an early colonizator.
Key characteristics
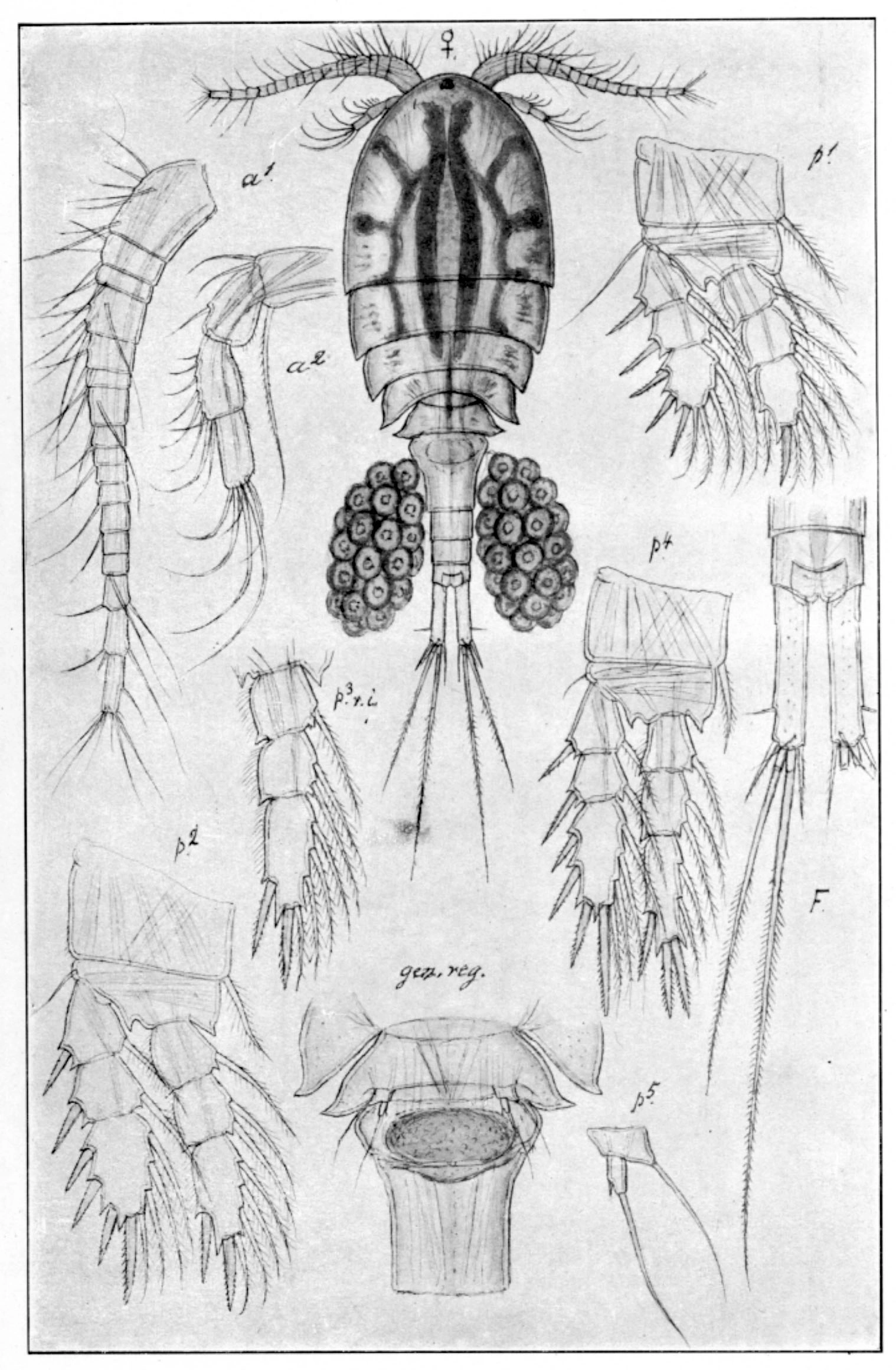
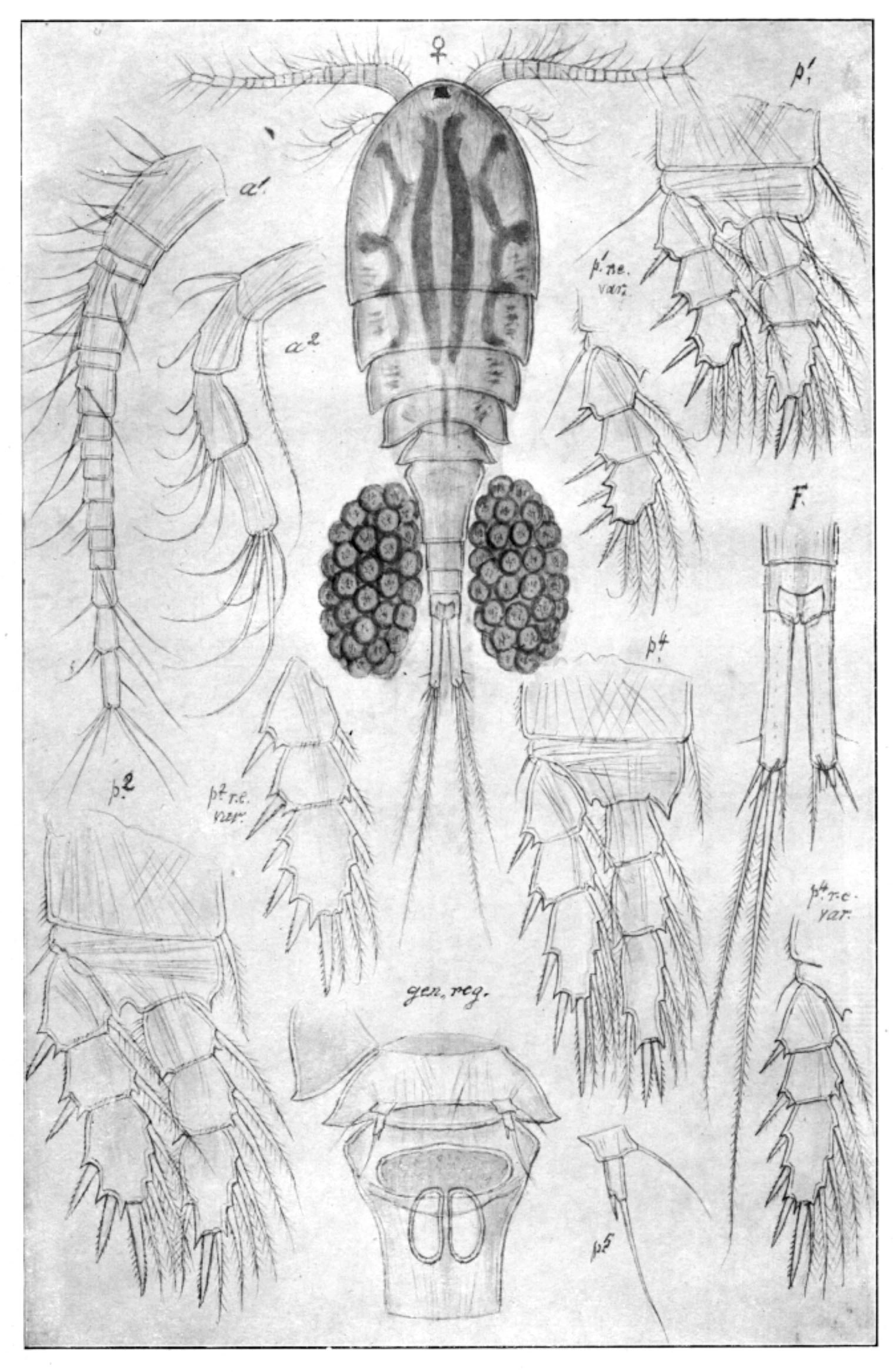
Acanthocyclops robustus (female)
The anterior part of A. robustus has an oval, somewhat robust form. Its furca is approximately 5 times as long as wide and the lateral seta is attached near the posterior end. The antennules are composed of 17 joints reaching to the first thorax segment. The spine formula of the last segment of the exopodite of the first to fourth pairs of legs is normally 3.4.4.4, but 2.3.3.3 may also occur. A. robustus may therefore be mixed up with A. vernalis. The colour is light yellowish brown.
Female: Length 1.05–1.50 mm
Male: Length smaller than the female
Ecology and distribution
A. robustus is a littoral copepod found in 14 % of the water bodies. It has a scattered distribution and is found in all parts of the country. In contrast to the other two Acanthocyclops species, most records are from lowland lakes (100–300 m a.s.l.). Though it is rare above 1000 m a.s.l it is found at 1271 m a.s.l. It occurs in waters of varying sizes, being most common in small ponds which it may invade a short time after they are established. Highest frequency is found in electrolyte rich water and in water with pH above 4.5.
Conductivity (m S/m)
Surface area (da)
Elevation (m a.s.l.)
Look alikes
Acanthocyclops vernalis