Diaphana glacialis
Shell description
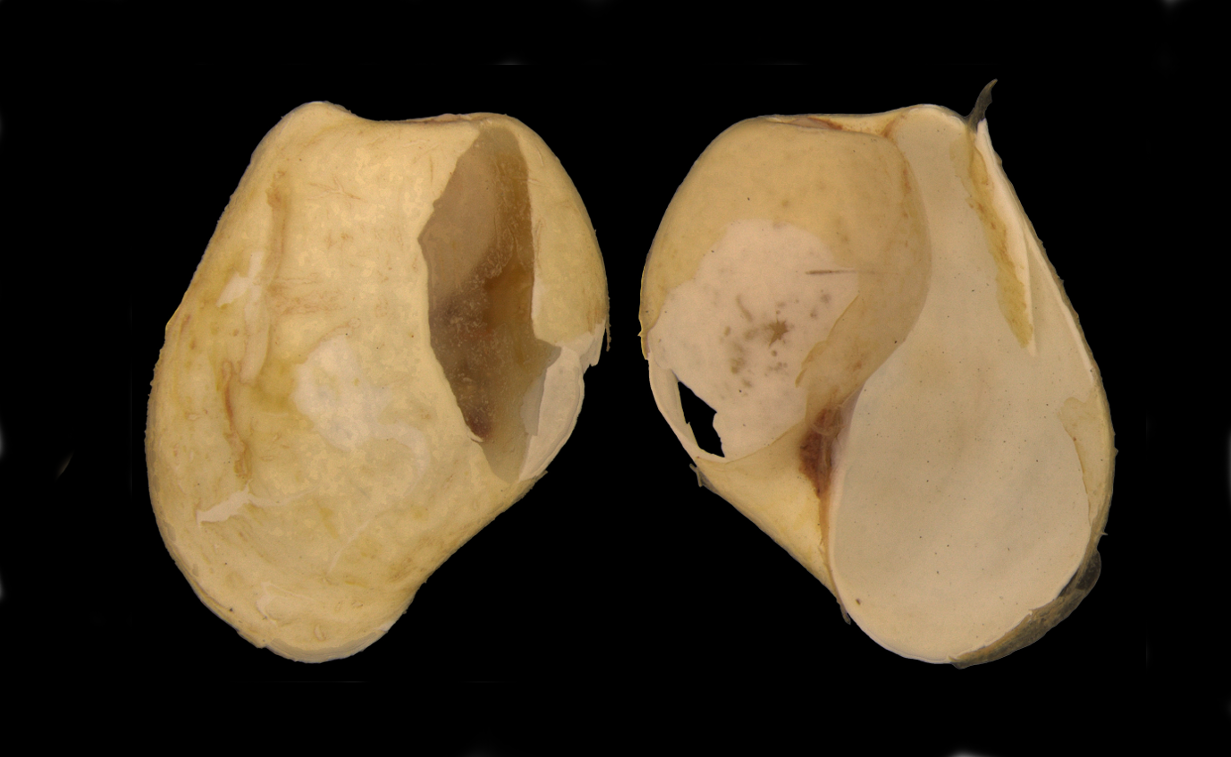
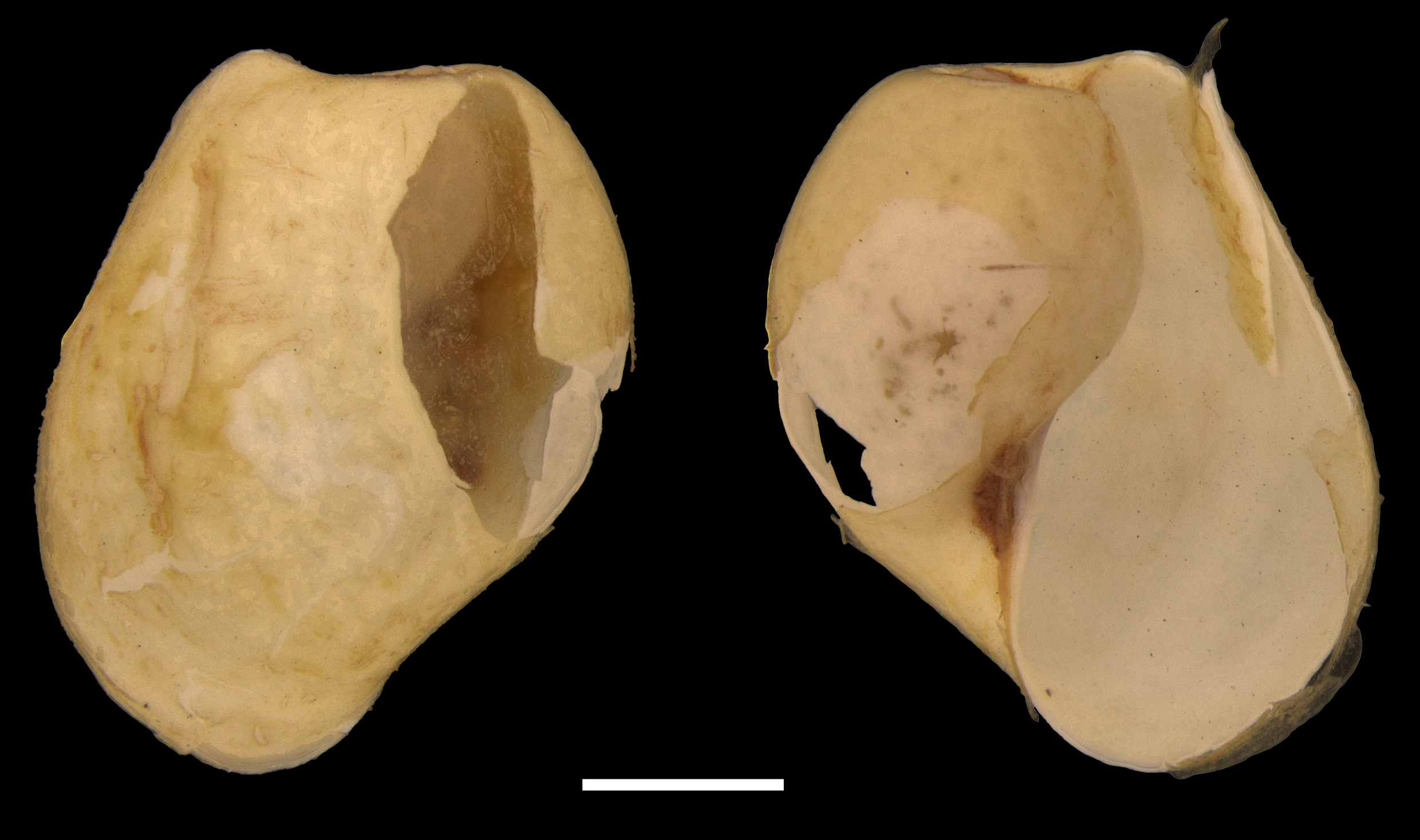
The shell is external and white in colour, usually with a globe-like shape. The outline narrows from the widest point in the middle of the shell towards the top, when the shell is viewed from above. The opening is large, and extends the length of the shell, narrowing towards the top. The top of the shell (apex) is blunted, and the oldest part of the shell (protoconch) extends slightly further out of the shell. The shell surface is smooth, with faint spiral lines. The length of the shell is 6 mm.
Animal description
The foot is branched in the hind part, and the eyes are visible in this species.
Anatomy
The radula consists of one inner lateral on each side and one central (rachidian) tooth. The outer lateral teeth are absent. The radula is asymmetric as the right lateral teeth are larger than the teeth on the left side of the radula. The male reproductive system consists of one thick and short prostate branch.
Ecology
Occurs at depths down to 240 m on mud, rocks with Psolus sea cucumbers, mud with shells, sand, stones, gravel, clay, mire and species of algae.
Geographical distribution
This species has a circumpolar distribution from the Beaufort Sea over Greenland and Svalbard to the Bering Sea.
Dorsal and ventral views of shell. Kings Bay, Svalbard. SMNH-type 4414. Scale bar = 1 mm.
References
Ohnheiser LT og Malaquias MAE (2014). The family Diaphanidae (Gastropoda: Heterobranchia: cephalaspidea) in Europe, with A redescription of the enigmatic species colobocephalus costellatus M. Sars, 1870. Zootaxa 6(3774): 501-522. http://zoobank.org/References/1C4C791C-09D7-4711-9D05-1ABE3DB24916 DOI: 10.11646/zootaxa.3774.6.1.